Introduction
Plasma, the often-overlooked liquid component of blood, harbours a wealth of proteins with remarkable healing potential. When carefully extracted and processed, these proteins become plasma-derived medicinal products (PDMPs) – life-altering treatments for a wide range of health conditions.

The Diverse Applications of Plasma-derived medicinal products (PDMPs)
Let's explore the specific ways PDMPs are used in medicine:
Strengthening Immunity: Immunoglobulins, a type of PDMP, provide concentrated antibodies to help fight infections. They are lifelines for people with primary immunodeficiencies (born with weak immune systems) and those whose immune systems are suppressed due to illness or medical treatments.
Controlling Bleeding: Clotting factors, such as Factor VIII for hemophilia A, are essential PDMPs. They help the blood clot normally, preventing dangerous bleeding episodes in people with bleeding disorders.
Taming Autoimmune Responses: In autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, the body attacks itself. Certain PDMPs can modulate the immune system, reducing inflammation and damage.
Managing Rare Conditions: Some genetic disorders cause a deficiency in specific plasma proteins. PDMPs replace these missing proteins, such as in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency where they protect the lungs.
Treating Shock and Trauma: Albumin, a key PDMP, maintains blood volume and pressure. It's critical after major blood loss from injuries, burns, or surgery.
Beyond the Basics: PDMPs have further uses, including treating neurological conditions, preventing Rh disease in newborns, and even combating rabies and snakebites.
The Science Behind PDMPs
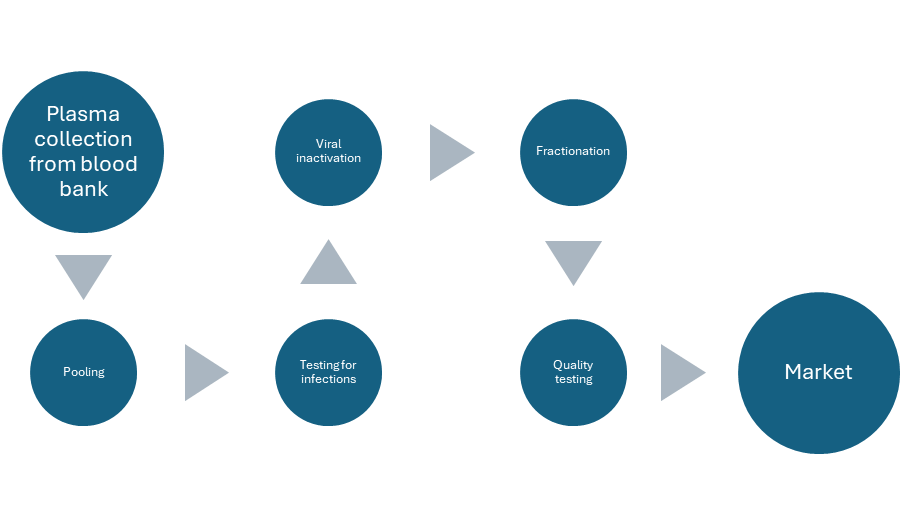
Donation: The Heart of It All: Healthy volunteers donate plasma through plasmapheresis, where blood is drawn, plasma is separated, and the rest returned to the donor. Or plasma from whole blood is collected from blood banks.

Pooling and Processing: Plasma from thousands of donations is pooled to ensure a large, consistent protein source. Then, advanced techniques like fractionation isolate specific proteins for different medicines.
Ensuring Safety: Manufacturers use rigorous viral inactivation and removal steps, making PDMPs extremely safe.
Formulation and Delivery: Purified proteins become injectable or intravenous solutions, tailored for various conditions.
Fractionation is the heart of creating PDMPs. This process involves separating the complex mixture of proteins within plasma into different portions, or fractions. Scientists use techniques that exploit differences in the proteins' size, charge, solubility, or other specific characteristics. Through careful fractionation, specific proteins needed for different therapies, like immunoglobulins, clotting factors, or albumin, can be isolated and purified for use in life-saving medicines.
Plasma Donation: A Gift of Life
Without plasma donors, PDMPs wouldn't exist. Donating plasma is a safe and impactful way to help others, especially for those who can donate frequently.
Major Categories of PDMPs
Immunoglobulins (Ig): Used to boost the immune system in various conditions.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG)
Specific Immunoglobulins (e.g., anti-tetanus, anti-rabies)
Coagulation Factors: Help control bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Factor VIII (for Hemophilia A)
Factor IX (for Hemophilia B)
Von Willebrand Factor (VWF)
Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (PCC)
Albumin: Maintains blood volume and pressure, used in shock, burns, and other situations.
Available in different concentrations (5%, 20-25%)
Other specialized PDMPs:
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency)
C1 Esterase Inhibitor (for Hereditary Angioedema)
Fibrinogen (for bleeding control)
Antithrombin (for preventing blood clots)
Important Notes:
This is not an exhaustive list. New PDMPs continue to be developed.
The specific products available and their indications may vary slightly depending on the country and regulatory approvals.
Expanding Knowledge
This is a deeper look at plasma-derived medicines, but there's still more to discover! Here are resources for further learning:
Plasma Protein Therapeutics Association (PPTA): https://www.pptaglobal.org/
[National Policy for Access to Plasma Derived Medicinal Products from Human Plasma for Clinical/Therapeutic Use - NACO] (https://naco.gov.in/sites/default/files/plasma%20policy_0.pdf)
[Information Sheet Ensuring the Quality and Safety of Plasma Derived Medicinal Products - World Health Organization] (https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/biologicals/blood-products/infosheet-plasma-derived.pdf?sfvrsn=9b6a9ca9_4&download=true)
Disclaimer: This blog is informational. Always seek personalized medical advice from your doctor.
Dr. Arun V J
MBBS, MD Transfusion Medicine
+91 8547415117


Comments